Threaded Mechanical Interface
CAD Design Documentation
Threaded Mechanical Interface
This project documents the design and assembly of a functional threaded mechanical interface consisting of a machined threaded component and a mating bolt. The objective was to model a realistic, manufacturable fastener system using proper mechanical design practices.
The work focuses on correct thread geometry, manufacturability, and assembly validation to reflect the decisions engineers make in automotive and aerospace programs.
Design Objectives
- Model a functional threaded interface with realistic geometry.
- Follow real-world fastener standards for pitch and engagement.
- Ensure manufacturability using conventional machining methods.
- Validate fit through a full CAD assembly.
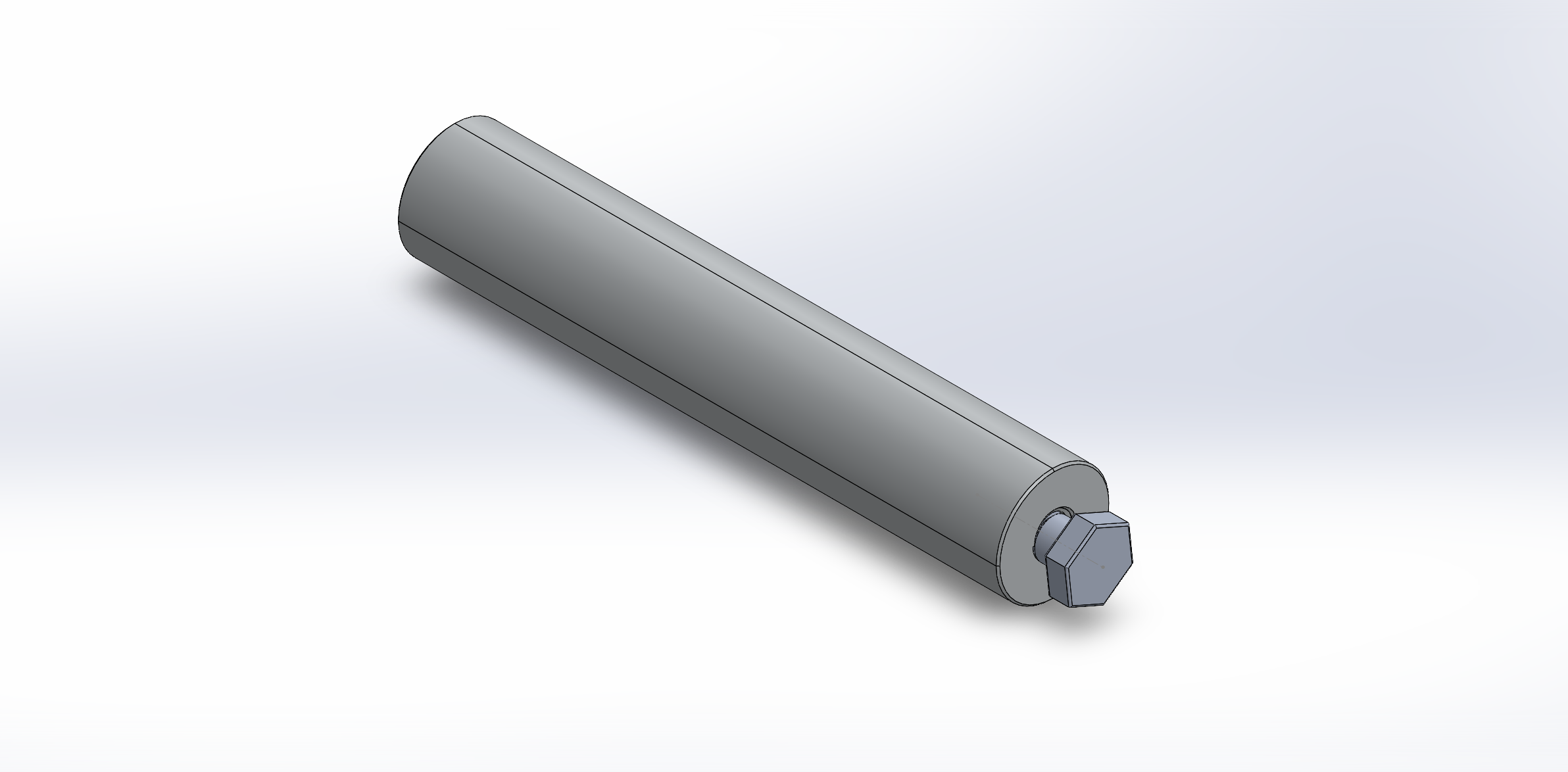
Threaded Component
Internal metric right-hand thread with appropriate engagement depth, lead-in chamfer, and softened external edges. Material: 6061-T6 aluminum.
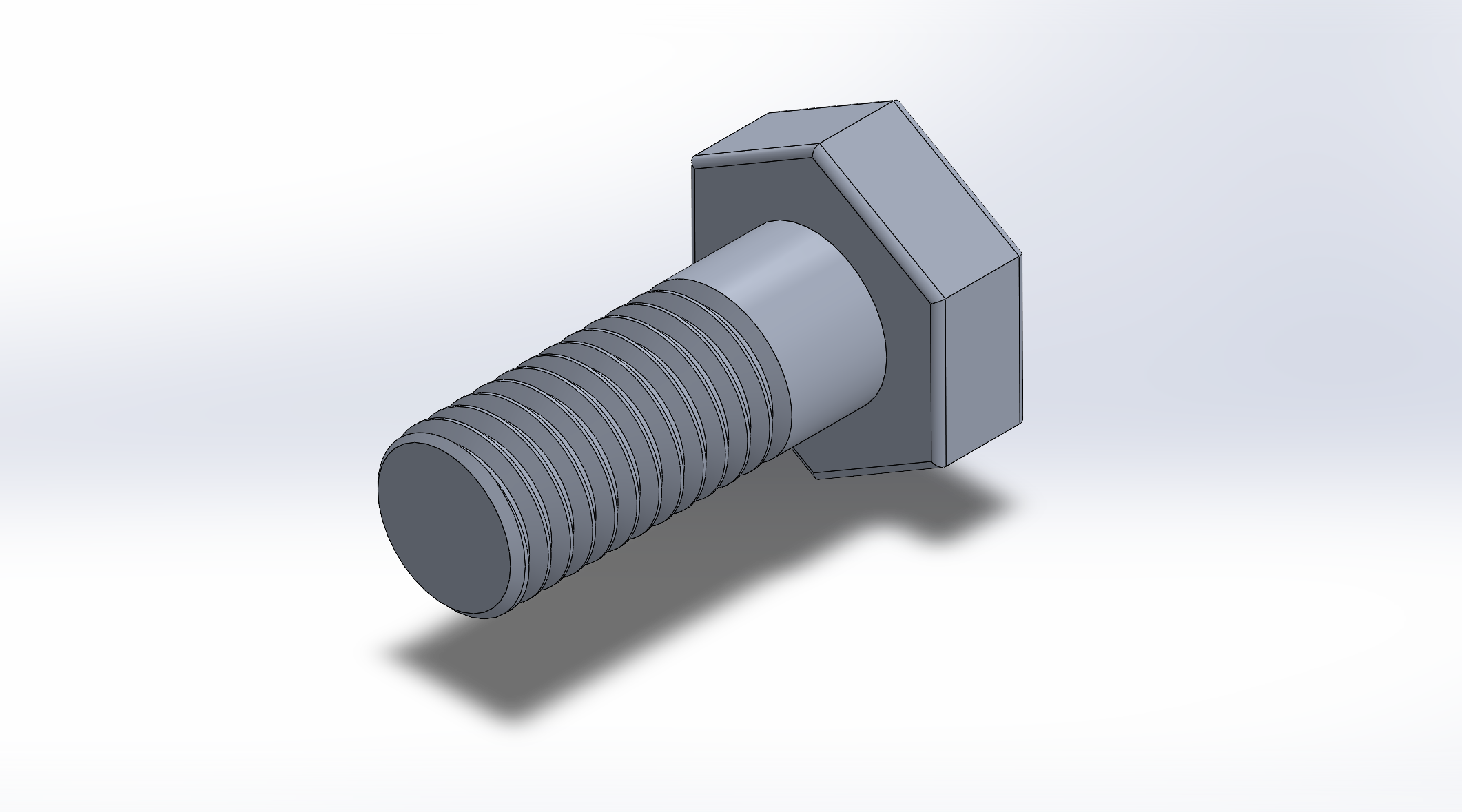
Bolt
External metric right-hand thread with matching pitch, lead chamfer, and standard head geometry. Material: automotive-grade steel.
Bolt and Threaded Component
Individual renders show the external metric bolt and the internal threaded component, highlighting thread lead-ins, chamfers, and edge softening for manufacturable geometry.
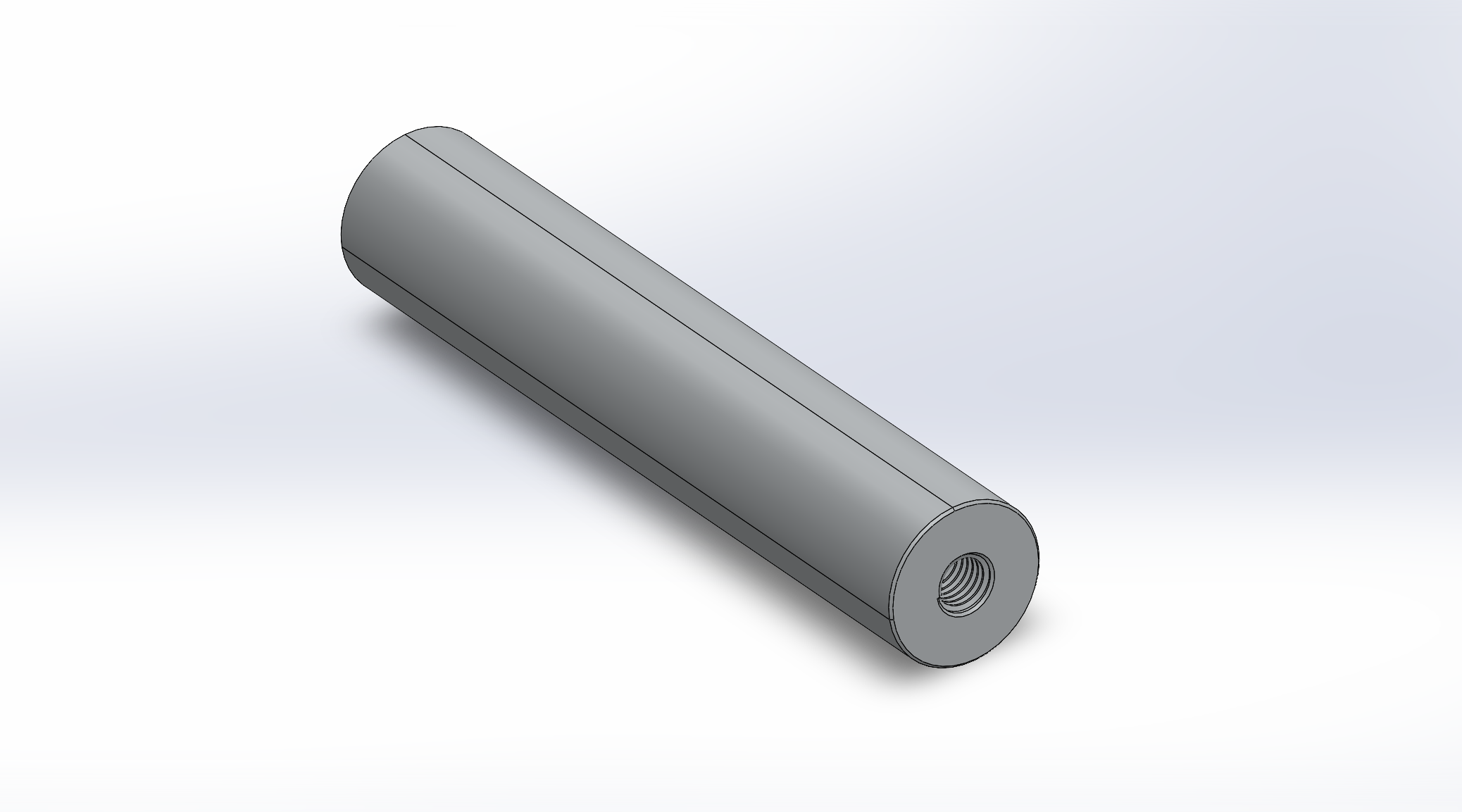

Threading & Manufacturing Considerations
Cut threads were used to represent realistic machining processes. Thread engagement depth was selected to prevent bottoming while maintaining structural integrity.
Chamfers were applied only at thread lead-ins to avoid interference with the thread geometry and to ease assembly.
Manufacturing Notes
- Metric right-hand thread profile.
- Lead-in chamfers only.
- Engagement depth sized for strength and clearance.
- Edges softened to reduce stress risers.
Assembly Validation
The components were assembled using concentric and coincident mates to verify alignment, fit, and functional compatibility. Rotation was constrained to represent a tightened fastener condition.
Why This Project Matters
This project demonstrates fundamental mechanical engineering skills including fastener design, manufacturability awareness, and assembly-level thinking applicable to automotive and aerospace systems.